Technology, social media and transactions over the Internet play key roles in how most organizations conduct business and reach out to prospective customers today. Those vehicles also serve as gateways to cyberattacks. Whether launched by run-of-the-mill hackers, criminals, insiders or even nation states, cyberattacks are likely to occur and can cause moderate to severe losses for organizations large and small. As part of a risk management plan, organizations routinely must decide which risks to avoid, accept, control or transfer. Transferring risk is where cyber insurance comes into play.
What constitutes a cyber attack?
Cyber attacks are socially or politically motivated attacks carried out primarily through the Internet. Attacks target the general public or national and corporate organizations and are carried out through the spread of malicious programs (viruses), unauthorized web access, fake websites, and other means of stealing personal or institutional information from targets of attacks, causing far-reaching damage.
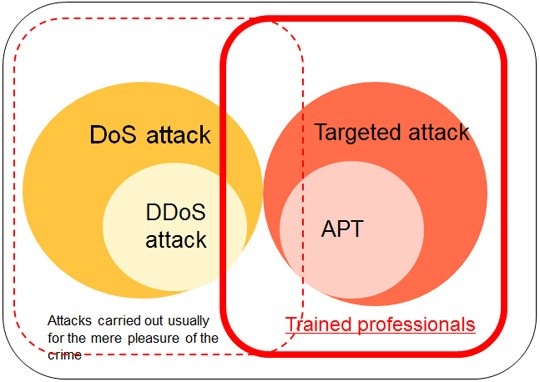
Types of Cyber Attacks
Targeted attack
Cyber attacks that are geared at particular organizations, services, and individuals to obtain private, technical, and institutional information, and other intellectual assets for the purpose of vandalism or monetary gain.
APT (Advanced Persistent Threat)
A kind of targeted attack geared at a particular entity and carried out continuously and persistently using a variety of means in order to gain access to the target. APTs are mainly divided into (1) attacks through public servers and public websites on the Internet and (2) attacks against users through social engineering of target users into sending malicious programs (typical example is targeted email attack).
DoS (Denial of Service) attack
an attack meant to disrupt services
DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attack
a DoS attack carried out from a distributed environment
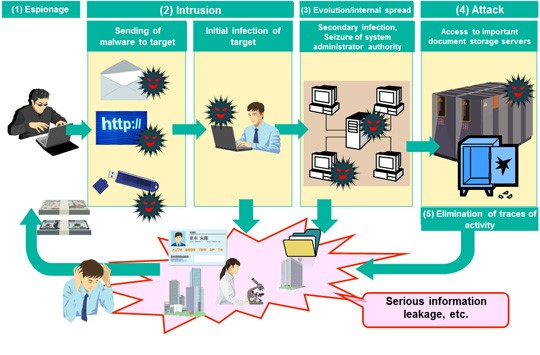
Overview of method used in targeted cyber attacks (typical)
Targeted attacks are becoming increasingly sophisticated as they go through different stages:
- Espionage
- Intrusion
- Internal spread
- Attack
- Elimination of traces of activity